Technical Profile
Introduction
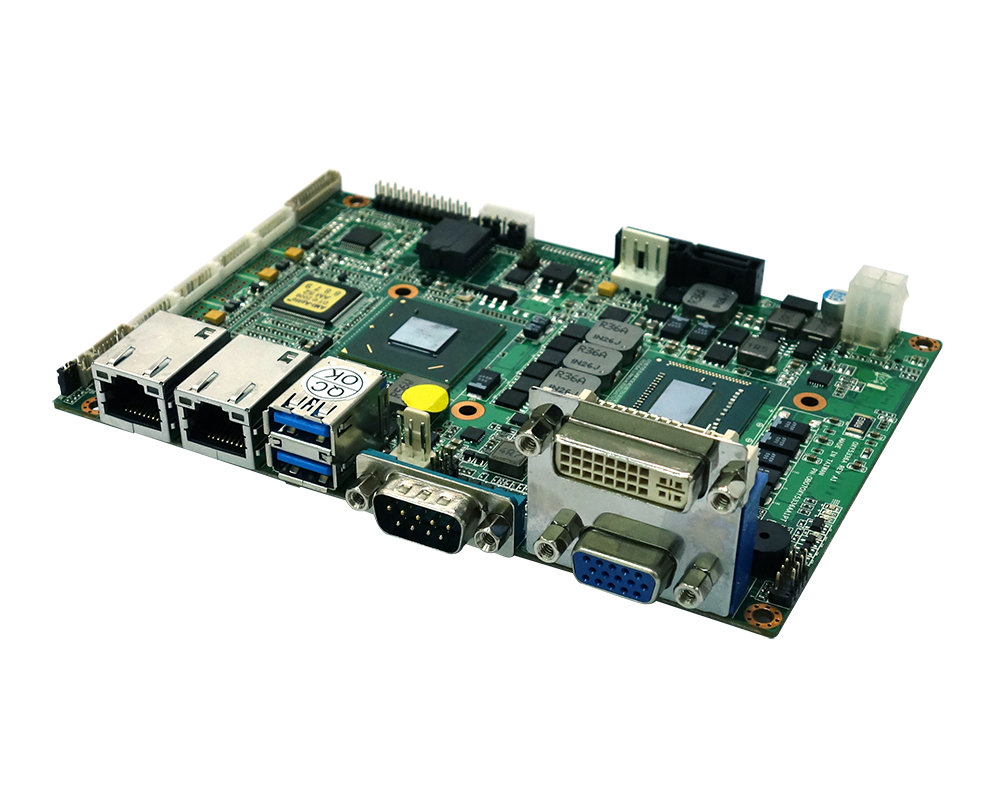
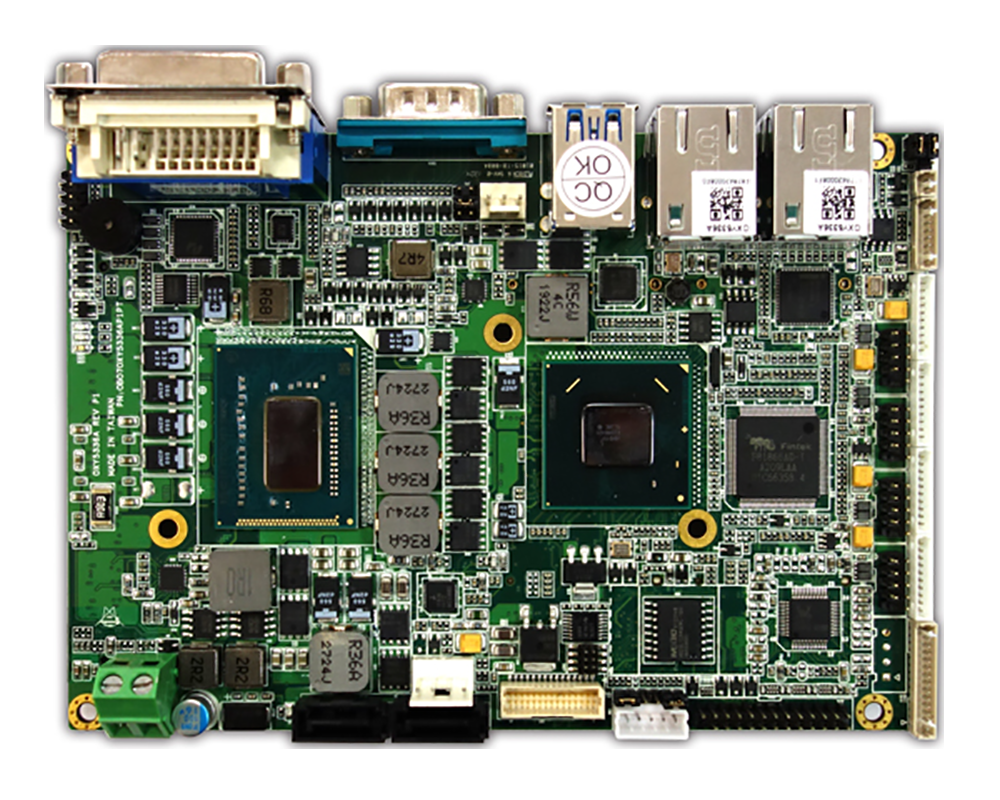
OXY5336A is a highly integrated 3.5” rugged SBC driven by Intel® 3rd generation Ivy Bridge CPU and chipset soldering onboard. Processor i7-3517UE plus Intel® HM76 chipset supports dual-core ULV 1.7 GHz, consuming only 17W and 4.1W individually. The powerful combination makes the SBC with high computing power for multi-tasking while reducing idle power consumption. Mission-critical applications can take the advantages of processors soldering onboard and extended operating temperature from -40 to 85°C to ensure ultimate durability, utmost resistance to shock & vibration. OXY5336A is truly a rugged SBC ideal for high-end Automation, heavy-duty railway, drilling and energy applications.

Thermal solution for fanless system design
Heat sinks are used to cool down device temperature by dissipating heat into surrounding air. Since the configurations and the power circuit placement of each model are different, which will lead to different extent of heat generation; therefore 7STARLAKE designs tailor-made heat sink for each motherboard. Special high and low fin design forms a wind-flow to reduce thermal resistance. Moreover, cross section wave line on the interface increases up to 30-40% air contact area. Combining these two features, thermal performance leverages to utmost. The option of fan is also available to the customers if fanless design is not necessary.
Advanced cooling solution for better heat dissipation
To meet the demands of customer’s extended temperature requirements, the whole thermal solution of OXY5336A simultaneously embraces two heat transfer methods, heat conduction and heat convection. For heat conduction, the solution utilizes a copper heat spreader on the bottom layer which directly contact with the processor and chipset. Heat is then transferred to upper aluminum heat sink. Regarding to heat convection, the temperature differences caused by high and low fin design forms a mild airflow that could bring away heat efficiently. Fan can also be an auxiliary by placing an appropriate sized fan on top of the heat sink. Breakdown drawing is provided as below.
Installation Instruction
Procedure: Stick thermal pad on CPU and chipset, and then simply put passive heat sink on thermal pad.
Copper heat spreader is used to contact with CPU and chipset directly to absorb heat efficiently on the bottom layer, and then spread the collected heat to upper aluminum heat sink. While aluminum is used to force heat convection. After heat spreader transfer heat from bottom layer to heat sink, High and low fin design plus wave line create airflow to dissipate heat.
Aluminum Passive Heat Sink
Heat sink is known for lowering the temperature by dissipating heat into the surrounding air. Though copper absorbs faster, it doesn’t dissipate faster than aluminum.
•It contains 96 % of aluminum, 30.8 mm height and weighs 321 g
•High and low fin design plus wave line increase contact surface up to 30-40% and create airflow.
•Consume shorter heat dissipating time owing to lower metal density
•Better performance in heat dissipating
Copper Flat Heat Spreader
Heat spreader is known for improving the distribution of heat. According to metal characteristics, copper has better heat absorption performance than aluminum. That is why copper is chosen to be heat spreader.
•It contains 99.9 % purity of copper, 5.5 mm height and weighs 326 g
•Absorb heat quicker than aluminum owing to higher heat conductivity coefficient (copper 402: aluminum 266)
•Better performance in heat absorbing
Synergies of copper heat spreader plus aluminum heat sink:
“Copper absorbs heat faster; aluminum dissipates heat faster”
Possessing the physical knowledge and expertise about metal characteristics accomplish the perfect match of thermal solution.
Operating Temp.
Can with stand extended temperature from -40°C to 85°C